LIMESTONE
In the commercial decorative stone trade, “marble” is
used to refer to a wide variety of relatively soft rocks (H = 3 to 5) that will
take a fine polish. These include true marbles and rocks that aren’t
marbles, such as limestones, tectonic breccias, and serpentinites. Shown
below are some limestones used as commercial “marble”. Limestones are
calcitic biogenic and ~chemical sedimentary rocks.

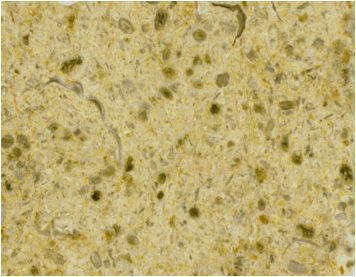
Jerusalem Limestone (field of view ~5.0 cm across) - a fossiliferous oolitic
limestone, widely used for centuries as a building stone in Jerusalem,
Israel. Several Cretaceous-aged marine limestones in Israel have been
& are quarried for building/decorative stone. Light from the setting
sun results in these rocks having the famous “Jerusalem Gold” color.
The sample shown above & below is a buff-colored,
fossiliferous oolitic limestone. Yaacov Arkin of the Israel Geological
Survey has kindly identified this rock as likely being "Mizzi Hilu"
(= “sweet rock” in Arabic) from the Zihor Formation (upper Judea Group,
Turonian, lower Upper Cretaceous).
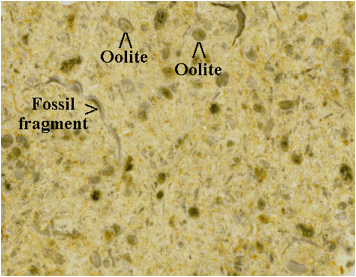
The small rounded structures in the limestone are
oolites. The narrow, curvilinear structures are shells and shell
fragments. The brownish, EKG-looking structure near the top of the above
photo is a stylolite (pressure-solution feature).
Jerusalem Limestone (field of view ~17.5 mm across).
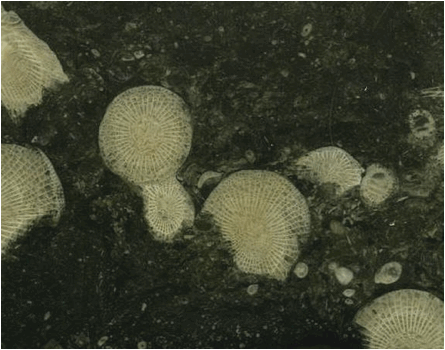
Frosterley Marble (12.5 cm across) - a fossiliferous limestone from
Rogerley Quarry at Frosterley, Durham County, northern England. The
large, light gray-brown colored, rounded objects in the rock are fossil rugose
corals (“horn corals”) - Dibunophyllum bipartitum (M'Coy, 1849)
(Animalia, Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Rugosa, Streptelasmatina, Zaphrenticae,
Aulophyllidae). This coral species is commonly encountered in the Great
Limestone, a lower Upper Mississippian unit (upper Visean Stage/upper
Asbian Stage, Lower Carboniferous, ~329-330 million years) in northern England.

Black & Gold Marble - a Triassic black micritic limestone from
northwestern Italy that has been extensively fractured (with white calcite vein
fillings), stylolitized, and partially dolomitized (the yellowish-brown
material). This rock is derived from the Portoro Limestone of the La
Spezia Formation (Rhaetian Stage, upper Upper Triassic, ~200-204 million years
old), from exposures in the Tuscan Nappe of Italy's Apennine Fold & Thrust
Belt. It's quarried at Porto Venere in eastern Liguria, northwestern
Italy.
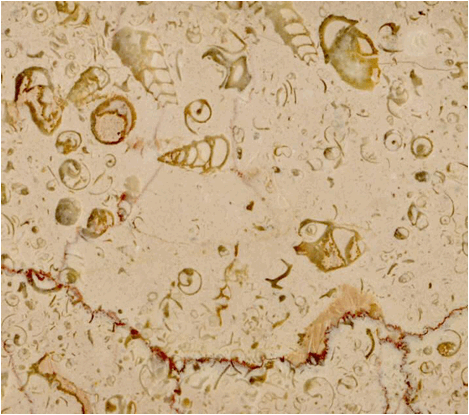
Here's a pinkish stylolitized fossiliferous limestone
with nice abundant fossil snail shells. I don't know the commercial name
or the provenance (if you recognize this, please let me know). The
stylolite is the reddish irregular line near the bottom. Stylolites are
the result of pressure solution. They are often present in limestones and
marbles in & near orogenic belts.
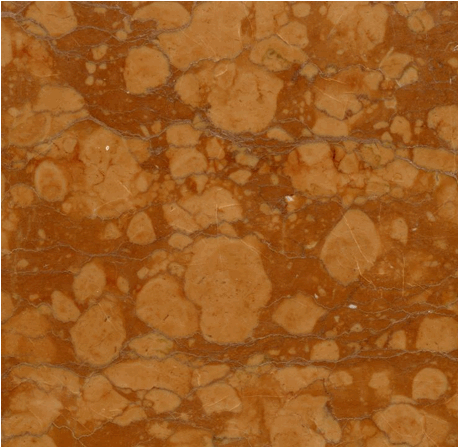
Rosso Verona Marble (a.k.a. “Red Verona Marble”) - a hematitic,
stylolitized, nodular limestone from the Jurassic of Verona Province in
northern Italy. The lighter-colored
areas (nodules) have been attributed to soft-sediment deformation (Pivko,
2003). Some samples have fossil
ammonite shells (Mollusca, Cephalopoda, Ammonoidea, Ammonitida). This limestone represents part of a
condensed succession of sediments deposited on an ancient submarine plateau,
the Trento Plateau.
Stratigraphy & Age: Rosso Ammonitico Superiore Member, Rosso Ammonitico
Formation, Oxfordian Stage, lower Upper Jurassic.
Locality:
commercial quarry near Caprino Veronese or Cerro Veronese or
Erbezzo or Sant’Ambrogio di Valpolicella, Verona Province, western
Veneto Region (Venetia Region), southern Alps, northern Italy.
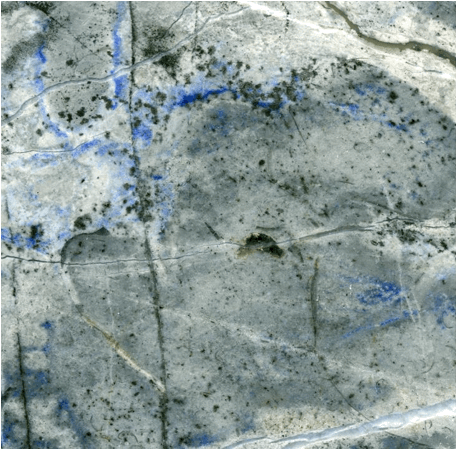
Lapis Eyes Limestone - a lazuritic-pyritic fossiliferous limestone from
the famous Flor de los Andes Lapis Lazuli Deposit in central Chile. The gray material that makes up the bulk
of this rock is marine fossiliferous limestone of Early Cretaceous age. It has been metamorphosed twice during
the Tertiary:
1) contact metamorphism by intrusion of monzogranites
of the Río Las Cuevas Granite (late Late Oligocene, 24 Ma);
2) sulfur-metasomatism by intrusion of dacites and
rhyodacties of the Portezuelo del Azufre Intrusion (late Middle Miocene to Late
Miocene, 9-13 Ma).
Neither of these metamorphic events has converted the
limestone to marble. The
sulfur-metasomatism event resulted in the formation of blue lazurite and
brassy-gold pyrite (= most of the very dark gray spots in the above
photo). Lazurite is a rare
metamorphic mineral ((Na1.5K0.2Ca1.2)(Al5.5Si6)(SO3,Sx,Cl1-x)). Rock-forming lazurite occurs at this
locality - lapis lazuli.
Afghanistan’s Hindu Kush Mountains are famous for having the
highest-quality lapis lazuli on Earth, but the Chilean deposit also has
high-quality material. The
perceived lower-quality material is cut & polished into decorative stone,
like this sample.
Stratigraphy & Age of Host Limestone: Río Tascadero Limestone, Berriasian Stage to
possibly Barremian Stage, lower Lower Cretaceous.
Locality:
Flor de los Andes Mine, in or near glacial cirque at the headwaters of
Lapislázuli Creek (a tributary of the Tascadero River), southeast of Ovalle
& northwest of Illapel, Coquimbo Region, Andes Mountains, near the border
with Argentina, central Chile (~31ľ 14’ 50.52” South, ~70ľ 32’ 10.73” West).